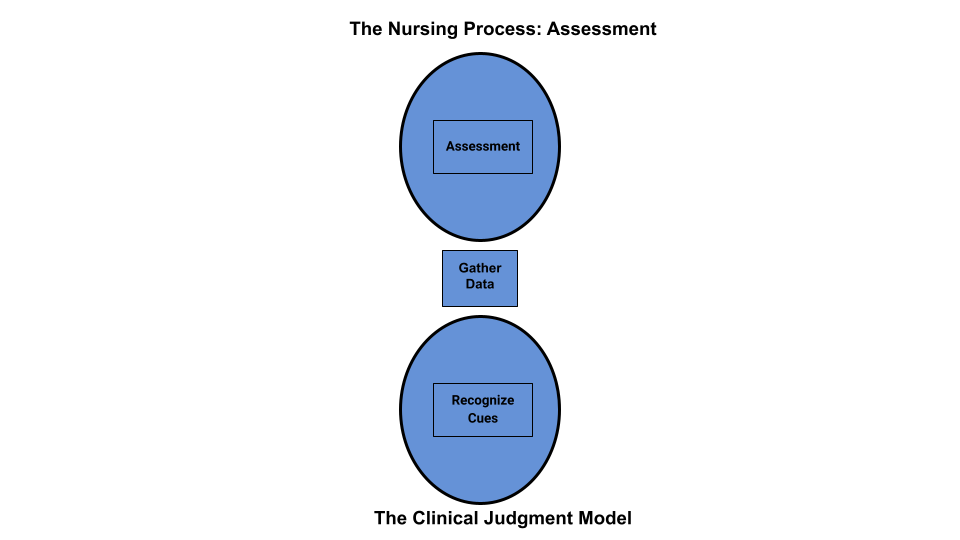

Assessment is the first step of the nursing process (and the first Standard of Practice by the American Nurses Association). This standard is defined as, “The registered nurse collects pertinent data and information relative to the health care consumer’s health or the situation.” This includes collecting “pertinent data related to the health and quality of life in a systematic, ongoing manner, with compassion and respect for the wholeness, inherent dignity, worth, and unique attributes of every person, including, but not limited to, demographics, environmental and occupational exposures, social determinants of health, health disparities, physical, functional, psychosocial, emotional, cognitive, spiritual/transpersonal, sexual, sociocultural, age-related, environmental, and lifestyle/economic assessments.” [1] See Figure 4.5a [2] for an illustration of how the Assessment phase of the nursing process corresponds to the NCSBN Clinical Judgment Measurement Model (NCJMM).

Nurses assess clients to gather information, then use critical thinking to analyze the data and recognized cues. Data is considered subjective or objective and can be collected from multiple sources.
Subjective data is information obtained from the client and/or family members and offers important cues from their perspectives. When documenting subjective data stated by a client, it should be in quotation marks and start with verbiage such as, “The client reports…” It is vital for the nurse to establish rapport with a client to obtain accurate, valuable subjective data regarding the mental, emotional, and spiritual aspects of their condition.
There are two types of subjective information, primary and secondary. Primary data is information provided directly by the client. Clients are the best source of information about their bodies and feelings, and the nurse who actively listens to a client will often learn valuable information while also promoting a sense of well-being. Information collected from a family member, chart, or other sources is known as secondary data. Family members can provide important information, especially for individuals with memory impairments, infants, children, or when clients are unable to speak for themselves.
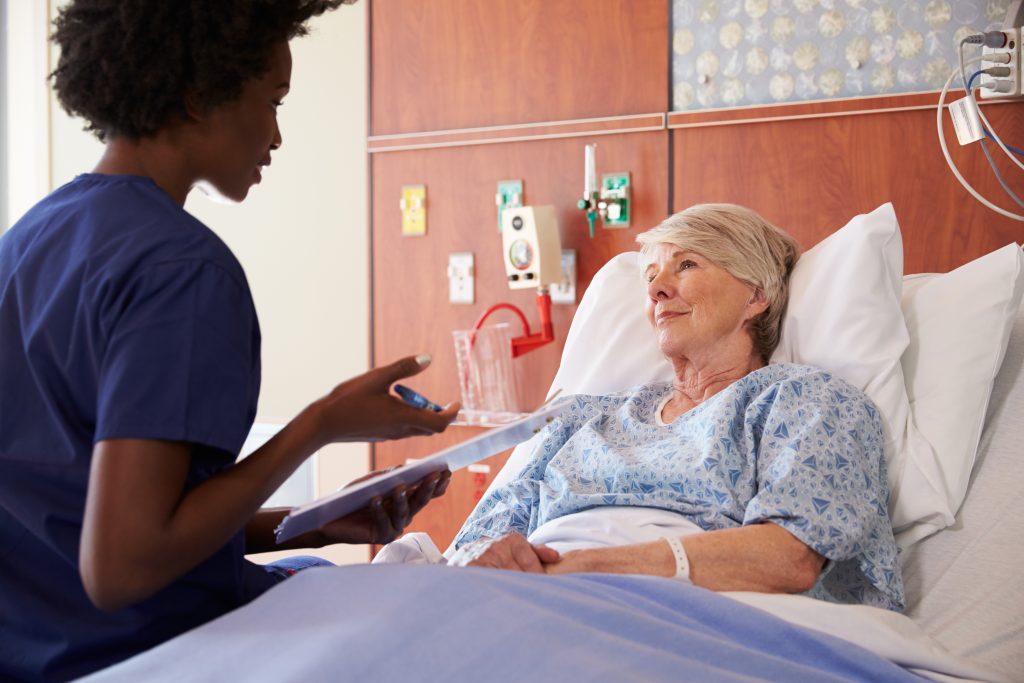
See Figure 4.5b [3] for an illustration of a nurse obtaining subjective data and establishing rapport after obtaining permission from the client to sit on the bed.
Example of Subjective Data
An example of how to document subjective data obtained during a client assessment is, “The client reports, ‘My pain is a level 2 on a 1-10 scale.’”

Objective Assessment Data
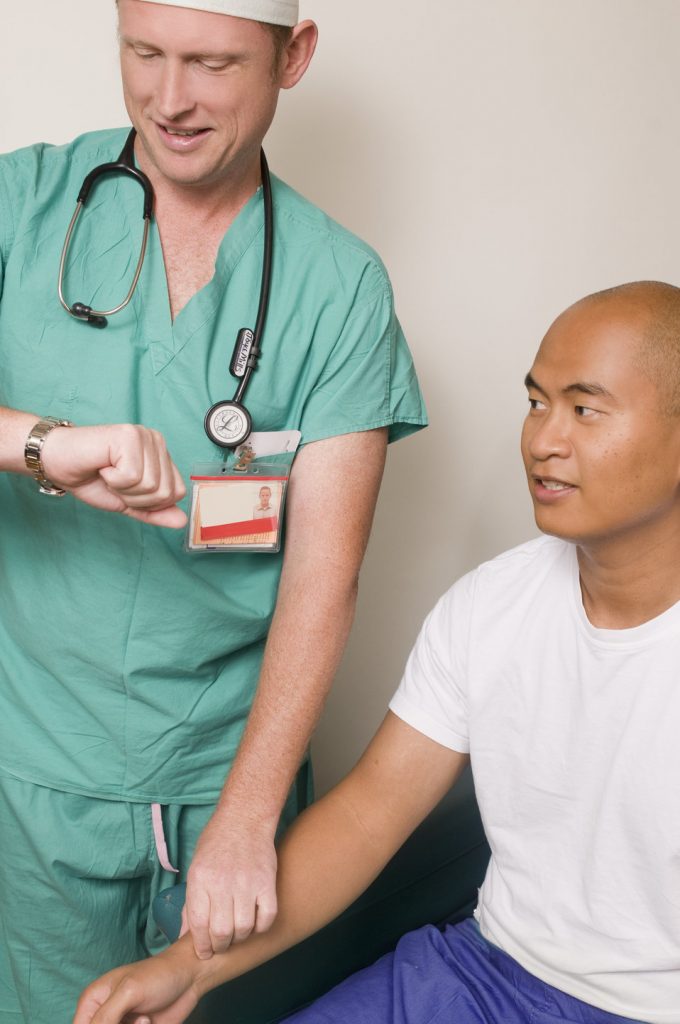
Objective data is anything that you can observe through your sense of hearing, sight, smell, and touch while assessing the client. Objective data is reproducible, meaning another person can easily obtain the same data. Examples of objective data are vital signs, physical examination findings, and laboratory results. See Figure 4.6 [4] for an image of a nurse performing a physical examination.
Example of Objective Data
An example of documented objective data obtained during a client assessment is, “The client’s radial pulse is 58 and regular, and their skin feels warm and dry.”
There are three sources of assessment data: interview, physical examination, and review of laboratory or diagnostic test results.
Interviewing includes asking the client and their family members questions, listening, and observing verbal and nonverbal communication. Reviewing the chart prior to interviewing the client may eliminate redundancy in the interview process and allows the nurse to hone in on the most significant areas of concern or need for clarification. However, if information in the chart does not make sense or is incomplete, the nurse should use the interview process to verify data with the client.
After performing client identification, the best way to initiate a caring relationship is to introduce yourself to the client and explain your role. Share the purpose of your interview and the approximate time it will take. When beginning an interview, it may be helpful to start with questions related to the client’s medical diagnoses. Medical diagnoses are diseases, disorders, or injuries diagnosed by a physician or advanced health care provider, such as a nurse practitioner or physician’s assistant. Reviewing the medical diagnoses allows the nurse to gather information about how they have affected the client’s functioning, relationships, and lifestyle. Listen carefully and ask for clarification when something isn’t clear to you. Clients may not volunteer important information because they don’t realize it is important for their care. By using critical thinking and active listening, you may discover valuable cues that are important to provide safe, quality nursing care. Sometimes nursing students can feel uncomfortable having difficult conversations or asking personal questions due to generational or other cultural differences. Don’t shy away from asking about information that is important to know for safe client care. Most clients will be grateful that you cared enough to ask and listen.
Be alert and attentive to how the client answers questions, as well as when they do not answer a question. Nonverbal communication and body language can be cues to important information that requires further investigation. A keen sense of observation is important. To avoid making inappropriate inferences, the nurse should validate cues for accuracy. For example, a nurse may make an inference that a client appears depressed when the client avoids making eye contact during an interview. However, upon further questioning, the nurse may discover that the client’s cultural background believes direct eye contact to be disrespectful and this is why they are avoiding eye contact. To read more information about communicating with clients, review the “Communication” chapter of this book.
A physical examination is a systematic data collection method of the body that uses the techniques of inspection, auscultation, palpation, and percussion. Inspection is the observation of a client’s anatomical structures. Auscultation is listening to sounds, such as heart, lung, and bowel sounds, created by organs using a stethoscope. Palpation is the use of touch to evaluate organs for size, location, or tenderness. Percussion is an advanced physical examination technique typically performed by providers where body parts are tapped with fingers to determine their size and if fluid or air are present. Detailed physical examination procedures of various body systems can be found in the Open RN Nursing Skills, 2e textbook with a head-to-toe checklist in Appendix C. Physical examination also includes the collection and analysis of vital signs.
Registered nurses (RNs) complete the initial physical examination and analyze the findings as part of the nursing process. Collection of follow-up physical examination data can be delegated to licensed practical nurses/licensed vocational nurses (LPNs/LVNs), or measurements such as vital signs and weight may be delegated to trained unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) when appropriate to do so. However, the RN remains responsible for supervising these tasks, analyzing the findings, and ensuring they are documented.
A physical examination can be performed as a comprehensive head-to-toe assessment or as a focused assessment related to a particular condition or problem. Assessment data is documented in the client’s medical record, either in their electronic medical record (EMR) or their paper chart, depending upon agency policies and procedures.
Reviewing laboratory and diagnostic test results provides relevant and useful information related to the needs of the client. Understanding how normal and abnormal results affect client care is important when implementing the nursing care plan and administering provider prescriptions. If results cause concern, it is the nurse’s responsibility to notify the provider and verify the appropriateness of prescriptions based on the client’s current status before implementing them.
Several types of nursing assessment are used in clinical practice:
Review Scenario C in the following box to apply concepts of assessment to a client scenario.
Scenario C [6]

Ms. J. is a 74-year-old woman who is admitted directly to the medical unit after visiting her physician because of shortness of breath, increased swelling in her ankles and calves, and fatigue. Her medical history includes hypertension (30 years), coronary artery disease (18 years), heart failure (2 years), and type 2 diabetes (14 years). She takes 81 mg of aspirin every day, metoprolol 50 mg twice a day, furosemide 40 mg every day, and metformin 2,000 mg every day.
Ms. J.’s vital sign values on admission were as follows:
Her weight is up 10 pounds since the last office visit three weeks prior. The client states, “I am so short of breath” and “My ankles are so swollen I have to wear my house slippers.” Ms. J. also shares, “I am so tired and weak that I can’t get out of the house to shop for groceries,” and “Sometimes I’m afraid to get out of bed because I get so dizzy.” She confides, “I would like to learn more about my health so I can take better care of myself.”
The physical assessment findings of Ms. J. are bilateral basilar crackles in the lungs and bilateral 2+ pitting edema of the ankles and feet. Laboratory results indicate a decreased serum potassium level of 3.4 mEq/L.
As the nurse completes the physical assessment, the client’s daughter enters the room. She confides, “We are so worried about mom living at home by herself when she is so tired all the time!”
Critical Thinking Questions
Answers are located in the Answer Key at the end of the book.
Data that the patient or family reports or data that the nurse makes as an inference, conclusion, or assumption, such as “the patient appears anxious.
× Close definitionInformation collected from the patient.
× Close definitionInformation collected from sources other than the patient.
× Close definitionData that the nurse can see, touch, smell, or hear or is reproducible such as vital signs. Laboratory and diagnostic results are also considered objective data.
× Close definitionA disease or illness diagnosed by a physician or advanced health care provider such as a nurse practitioner or physician’s assistant. Medical diagnoses are a result of clustering signs and symptoms to determine what is medically affecting an individual.
× Close definitionInterpretations or conclusions based on cues, personal experiences, preferences, or generalizations.
× Close definitionA systematic data collection method of the body that uses the techniques of inspection, auscultation, palpation, and percussion.
× Close definitionA nurse who has had a designated amount of education and training in nursing and is licensed by the State Board of Nursing.
× Close definitionNurses that have had specific training and passed a licensing exam. The training is generally less than that of a Registered Nurse. The scope of practice of a LPN/LVN is determined by the facility and the state’s Nurse Practice Act.
× Close definitionAny unlicensed personnel trained to function in a supportive role, regardless of title, to whom a nursing responsibility may be delegated.
× Close definitionAn electronic version of the patient’s medical record.
× Close definitionNursing Fundamentals 2e Copyright © by Open Resources for Nursing (Open RN) is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, except where otherwise noted.